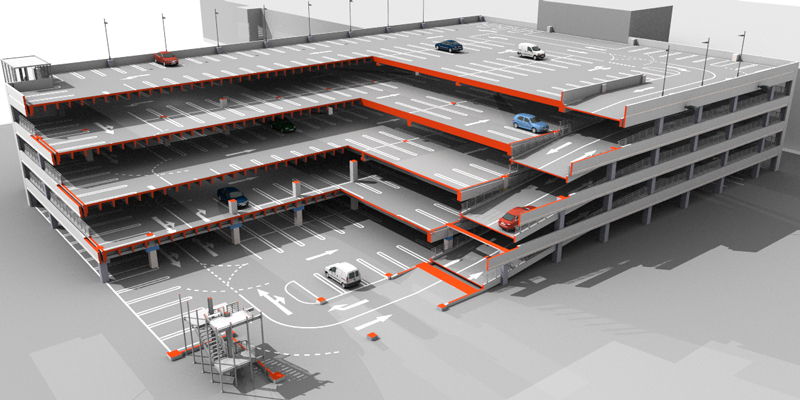
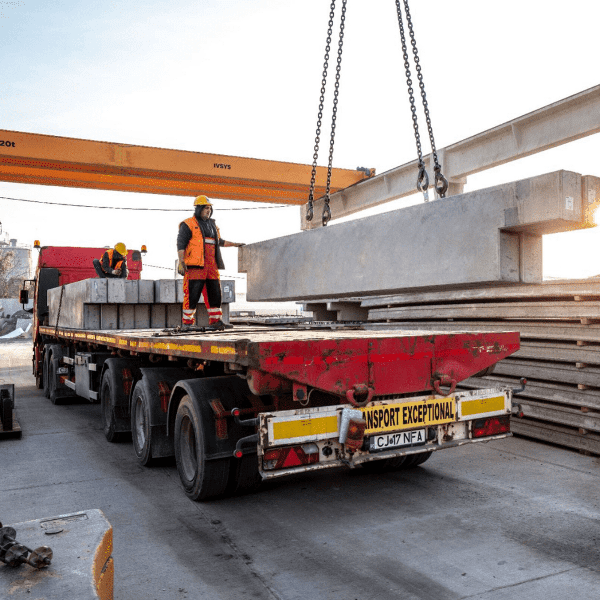
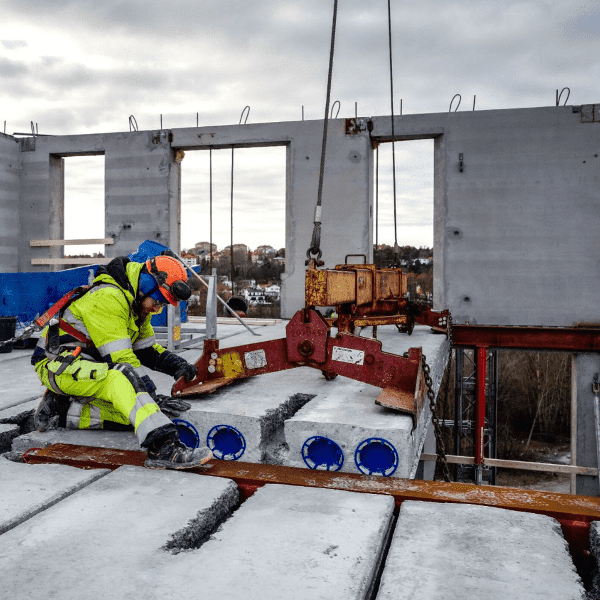
Fast set-up
Constructing with precast reinforced concrete elements saves a considerable amount of time. The proportion of work at the construction site is small – while preparations and foundations are being made at the construction site, the elements of the car park are being manufactured at the plant. Since it is a mass production and the time period for assembly is short, it saves a lot of time. It is possible to build approximately 1,000-1,500 m in a week.
Elements are like Lego bricks which can be used to quickly assemble buildings of different shapes. The plant-made solution has many advantages compared to cast-in-situ solutions.
Quality
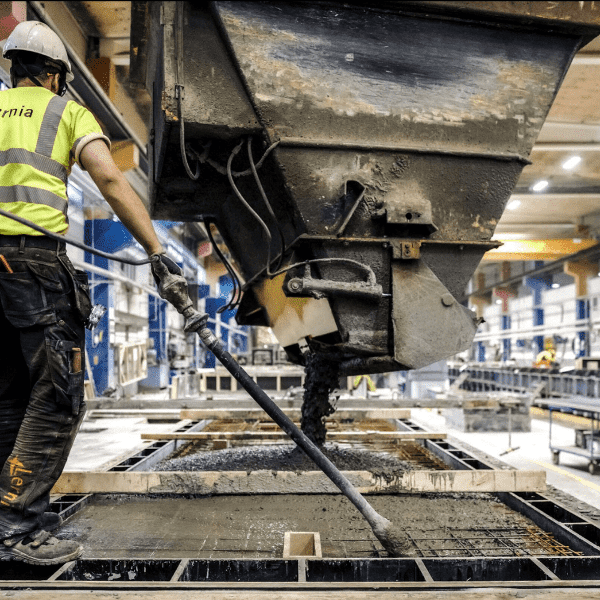
The element solution ensures a high-quality result, since the all-year-round conditions are considerably better at the factory than at the construction site. Factory’s controlled conditions make it easy to manufacture high quality concrete and ensure the desired properties of the material. Concrete itself is very resistant in a chemically aggressive environment.
Fewer columns reduce fear of parking
A car park made of precast concrete elements is spacious – there are no columns which would make parking more complicated. The number of columns in the building is smaller due to long-span prestressed concrete panels. This way, the space under the roof is not filled with columns which would otherwise limit the use of space.
Many different finishing possibilities
The possibilities of concrete as a material are diverse. Various relief shapes, stone colours and treatments can be used to make the surface of concrete interesting and original.
The first principle of planning a car park is the following: “A car park must allow convenient parking and should not be an emergency solution for a driver unable to find a parking space elsewhere.” An efficient car park is convenient and easy to use. Constant fender-benders and jams in a car park indicate faulty planning.
The planning and design of car parks is a technical process which requires careful analysis. The planning process should involve the evaluation of parking demand, the needs of users, and volume of traffic flow. In order to avoid jams and dangerous situations at crossing points, it is important to analyse the existing traffic management and access of cars to the car park. In order to ensure optimum convenience for the users, the internal logic and operating mode of the building should be taken into consideration.
Waiting queues indicate faulty planning
The internal logic of car parks is completely different from other types of buildings: moving around in a car park must be convenient for both pedestrians and drivers. When planning a car park, it should be ensured that entering and exiting the car park is as fast as possible. Clear marking and direction signs are of course necessary. It is important to consider the traffic management around the car park. Cars entering and exiting the car park should not create waiting queues and should blend in with the city traffic; the car park must be easily accessible and its entries and exits should be logically placed in terms of the city roads.
Inconvenient posts and narrow pathways are a thing of the past
When designing the building, it would be reasonable not to save space at the expense of the size of parking spaces. Parking is comfortable when the spaces are large enough, the levels do not have inconvenient posts, and the pathways are wide. When drivers have clear sight, traffic in the car park becomes safer.
Pedestrians must be able to move safely in the car park. Stairs and elevators are planned at the proximity of the parking area. Separating pedestrian pathways from the carriageway must also be considered and, in shopping centres, the possibility to move around easily with large shopping carts must be ensured.
Friendly-looking car parks attract users
A car park is an artificial environment. When its location, architectural solutions and operating mode are not thought through, the car park seems unattractive and people prefer parking elsewhere. A well planned car park is user-friendly.
Simple suggestions
A desolate car park full of cars does not seem so bleak when there is background music and sunlight. In order to avoid dark corners, good general lighting is important besides the sunlight.
Automatic pay stations or service points should be clearly visible and located in an open space. Markings that regulate traffic should be unequivocal, entries and exits should be easy to find. Massive partitions as well as nooks and corners at parking areas should be avoided.
Although, at first sight, it may seem that a car park has a monotonous appearance from the outside and it is difficult to combine with its surroundings, original solutions are possible here as well. Supporting structure can be hidden or, on the contrary, uncovered and accentuated. For example, when building barriers, other possible solutions besides concrete include metal, wood or glass.
Effective use of space is essential when designing a car park: it should hold as many cars as possible while making parking comfortable. For evaluating the efficiency of the use of space, it is calculated how many square metres of total space corresponds to one parking space. When comparing different car parks, the following should be taken into account:
- calculations are based on the same grounds. Usually, the maximum dimensions are used as bases, including the carriageways, slip roads and staircases;
- the relative size of the building: the smaller the building, the bigger portion of its floor space is under slip roads, carriageways and staircases;
- the size of the “reference car” should be determined.
Usually, 27-30 square metres of total space are needed for one parking space. This indicator depends on the size and shape of the car park, the shape of the lot, existence of additional slip roads for facilitating traffic, etc. The price of the car park depends on whether it is built partially underground or not. The first underground storey is approximately 1.5 times more expensive than the first storey on the ground, and the second underground storey is 1.5 times more expensive than the first underground storey.
E-Betoonelement: car parks from planning to construction
E-Betoonelement takes the full responsibility regarding production of concrete elements.
Full contracting offered includes the following:
– consultations on the solution of precast element car park;
– compiling the solution and technical design;
– production of elements and transport to the construction site;
– assembly of the car park;
– design and completion of cast-in-situ topping on reinforced concrete floors.
E-Betoonelement takes the responsibility for the majority of construction risks as well as for completing the support structure of the building. In the case of car parks, the full contracting of precast concrete structure constitutes more than half of the volume and cost of the construction contracting. It is important to weigh different options and find the best solution.
All works, starting from the design and ending with the delivery of precast reinforced concrete constructions, are managed by the project manager at E-Betoonelement. This ensures quick exchange of information and the client can turn to one person with all questions.
E-Betoonelement is part of the international group Consolis SAS which offers prefabricated concrete products and related services in most European countries. The undertakings of the group have been manufacturing precast concrete car parks for 50 years; therefore, E-Betoonelement has had a good opportunity to learn from the experience of its colleagues.
Parking platform – a simple and cheap solution
Parking platform is a level above the ground which is very simple in its essence – cars can be parked on the street level, that is, on the first storey, and on the second storey, that is, on the platform. When car parks are multi-storey buildings designed to accommodate a large number of cars, then platforms are suitable for relatively small offices or service companies that need to separate parking from street level. Platforms have a simple structure and they are usually quite small. Platforms are easy to build and to expand if foreseen in the design phase.

Continuously rising car park – plenty of space and great capacity
In a continuously rising car park, cars are parked on sloping floors which also connect the storeys. The advantage of this solution is the car park’s great capacity, therefore making it suitable for congested areas. This type of car park should be used in limited urban space – for example, at office buildings, hotels and other non-residential buildings.

Mezzanine car park – economical structure and excellent use of space
Storeys of a mezzanine car park are divided in two and are vertically shifted towards each other. The connection between storeys consists of short slip roads which allow using the space economically. Cars are parked on horizontal surface. This is the most flexible solution – it is used for small, medium and large car parks. This solution is suitable for office buildings, apartment buildings and smaller shopping centres.

Single level car park– excellent capacity
Single level car parks are characterised by long slip roads and large parking spaces. Making this solution pay off requires a large construction area. On the other hand, the structure is simple and easy to build. Car parks of this type usually have three to five storeys. The solution is suitable for medium and large car parks – for example, at hotels, shopping centres and airports.
Underground car park– possible solution for lack of space
Building parking lots under squares, roads and parks is technically much more complex than a construction on the ground. Underground car parks are closed structures and, in order to support the structure, it is necessary to build supporting walls, install enough supporting columns and ensure efficient water insulation. In addition to that, mechanical ventilation, fire fighting and security systems must be put in place. Due to technical complexity, this system is also more expensive; therefore, building an underground car park is reasonable only when there is not enough free space to build the car park on the ground.
PARKING GARAGE — HENRY FORD's modern dream
When Henry Ford announced in 1907 that he is going to make a car that is affordable to common people, there were many who doubted his words. He and other car manufacturers managed to do it nevertheless; today, the number of passenger cars in the world has reached 600 million.
Thousands of cars need thousands of parking spaces. There are not enough parking spaces in cities and settlements and, thus, the space in front of the houses is packed with cars. Additional parking space can be created only at the expense of sports grounds and playgrounds.
When arriving in a city by car, finding a parking space can be a real challenge since there are simply not enough parking spaces next to the sidewalks. Enterprises are also moving to the outskirts of cities or even beyond city borders because of the lack of parking spaces, making people even more dependent on cars.
Nobody had even heard of car parks in the 19th century. Today, incorporating parking areas and car parks into the city plan is one possibility to reduce the number of cars parked on city streets and courtyards – nobody wants to look out the window and only see a huge parking lot, to drive in circles in streets filled with cars, looking for a parking space, or walk on a sidewalk which is increasingly occupied by cars.
Fast set-up
Constructing with precast reinforced concrete elements saves a considerable amount of time. The proportion of work at the construction site is small – while preparations and foundations are being made at the construction site, the elements of the car park are being manufactured at the plant. Since it is a mass production and the time period for assembly is short, it saves a lot of time. It is possible to build approximately 1,000-1,500 m in a week.
Elements are like Lego bricks which can be used to quickly assemble buildings of different shapes. The plant-made solution has many advantages compared to cast-in-situ solutions.
Quality
The element solution ensures a high-quality result, since the all-year-round conditions are considerably better at the factory than at the construction site. Factory’s controlled conditions make it easy to manufacture high quality concrete and ensure the desired properties of the material. Concrete itself is very resistant in a chemically aggressive environment.
Fewer columns reduce fear of parking
A car park made of precast concrete elements is spacious – there are no columns which would make parking more complicated. The number of columns in the building is smaller due to long-span prestressed concrete panels. This way, the space under the roof is not filled with columns which would otherwise limit the use of space.
Many different finishing possibilities
The possibilities of concrete as a material are diverse. Various relief shapes, stone colours and treatments can be used to make the surface of concrete interesting and original.
The first principle of planning a car park is the following: “A car park must allow convenient parking and should not be an emergency solution for a driver unable to find a parking space elsewhere.” An efficient car park is convenient and easy to use. Constant fender-benders and jams in a car park indicate faulty planning.
The planning and design of car parks is a technical process which requires careful analysis. The planning process should involve the evaluation of parking demand, the needs of users, and volume of traffic flow. In order to avoid jams and dangerous situations at crossing points, it is important to analyse the existing traffic management and access of cars to the car park. In order to ensure optimum convenience for the users, the internal logic and operating mode of the building should be taken into consideration.
Waiting queues indicate faulty planning
The internal logic of car parks is completely different from other types of buildings: moving around in a car park must be convenient for both pedestrians and drivers. When planning a car park, it should be ensured that entering and exiting the car park is as fast as possible. Clear marking and direction signs are of course necessary. It is important to consider the traffic management around the car park. Cars entering and exiting the car park should not create waiting queues and should blend in with the city traffic; the car park must be easily accessible and its entries and exits should be logically placed in terms of the city roads.
Inconvenient posts and narrow pathways are a thing of the past
When designing the building, it would be reasonable not to save space at the expense of the size of parking spaces. Parking is comfortable when the spaces are large enough, the levels do not have inconvenient posts, and the pathways are wide. When drivers have clear sight, traffic in the car park becomes safer.
Pedestrians must be able to move safely in the car park. Stairs and elevators are planned at the proximity of the parking area. Separating pedestrian pathways from the carriageway must also be considered and, in shopping centres, the possibility to move around easily with large shopping carts must be ensured.
Friendly-looking car parks attract users
A car park is an artificial environment. When its location, architectural solutions and operating mode are not thought through, the car park seems unattractive and people prefer parking elsewhere. A well planned car park is user-friendly.
Simple suggestions
A desolate car park full of cars does not seem so bleak when there is background music and sunlight. In order to avoid dark corners, good general lighting is important besides the sunlight.
Automatic pay stations or service points should be clearly visible and located in an open space. Markings that regulate traffic should be unequivocal, entries and exits should be easy to find. Massive partitions as well as nooks and corners at parking areas should be avoided.
Although, at first sight, it may seem that a car park has a monotonous appearance from the outside and it is difficult to combine with its surroundings, original solutions are possible here as well. Supporting structure can be hidden or, on the contrary, uncovered and accentuated. For example, when building barriers, other possible solutions besides concrete include metal, wood or glass.
Effective use of space is essential when designing a car park: it should hold as many cars as possible while making parking comfortable. For evaluating the efficiency of the use of space, it is calculated how many square metres of total space corresponds to one parking space. When comparing different car parks, the following should be taken into account:
- calculations are based on the same grounds. Usually, the maximum dimensions are used as bases, including the carriageways, slip roads and staircases;
- the relative size of the building: the smaller the building, the bigger portion of its floor space is under slip roads, carriageways and staircases;
- the size of the “reference car” should be determined.
Usually, 27-30 square metres of total space are needed for one parking space. This indicator depends on the size and shape of the car park, the shape of the lot, existence of additional slip roads for facilitating traffic, etc. The price of the car park depends on whether it is built partially underground or not. The first underground storey is approximately 1.5 times more expensive than the first storey on the ground, and the second underground storey is 1.5 times more expensive than the first underground storey.
E-Betoonelement: car parks from planning to construction
E-Betoonelement takes the full responsibility regarding production of concrete elements.
Full contracting offered includes the following:
– consultations on the solution of precast element car park;
– compiling the solution and technical design;
– production of elements and transport to the construction site;
– assembly of the car park;
– design and completion of cast-in-situ topping on reinforced concrete floors.
E-Betoonelement takes the responsibility for the majority of construction risks as well as for completing the support structure of the building. In the case of car parks, the full contracting of precast concrete structure constitutes more than half of the volume and cost of the construction contracting. It is important to weigh different options and find the best solution.
All works, starting from the design and ending with the delivery of precast reinforced concrete constructions, are managed by the project manager at E-Betoonelement. This ensures quick exchange of information and the client can turn to one person with all questions.
E-Betoonelement is part of the international group Consolis SAS which offers prefabricated concrete products and related services in most European countries. The undertakings of the group have been manufacturing precast concrete car parks for 50 years; therefore, E-Betoonelement has had a good opportunity to learn from the experience of its colleagues.
Parking platform – a simple and cheap solution
Parking platform is a level above the ground which is very simple in its essence – cars can be parked on the street level, that is, on the first storey, and on the second storey, that is, on the platform. When car parks are multi-storey buildings designed to accommodate a large number of cars, then platforms are suitable for relatively small offices or service companies that need to separate parking from street level. Platforms have a simple structure and they are usually quite small. Platforms are easy to build and to expand if foreseen in the design phase.

Continuously rising car park – plenty of space and great capacity
In a continuously rising car park, cars are parked on sloping floors which also connect the storeys. The advantage of this solution is the car park’s great capacity, therefore making it suitable for congested areas. This type of car park should be used in limited urban space – for example, at office buildings, hotels and other non-residential buildings.

Mezzanine car park – economical structure and excellent use of space
Storeys of a mezzanine car park are divided in two and are vertically shifted towards each other. The connection between storeys consists of short slip roads which allow using the space economically. Cars are parked on horizontal surface. This is the most flexible solution – it is used for small, medium and large car parks. This solution is suitable for office buildings, apartment buildings and smaller shopping centres.

Single level car park– excellent capacity
Single level car parks are characterised by long slip roads and large parking spaces. Making this solution pay off requires a large construction area. On the other hand, the structure is simple and easy to build. Car parks of this type usually have three to five storeys. The solution is suitable for medium and large car parks – for example, at hotels, shopping centres and airports.

Underground car park– possible solution for lack of space
Building parking lots under squares, roads and parks is technically much more complex than a construction on the ground. Underground car parks are closed structures and, in order to support the structure, it is necessary to build supporting walls, install enough supporting columns and ensure efficient water insulation. In addition to that, mechanical ventilation, fire fighting and security systems must be put in place. Due to technical complexity, this system is also more expensive; therefore, building an underground car park is reasonable only when there is not enough free space to build the car park on the ground.
PARKING GARAGE — HENRY FORD's modern dream
When Henry Ford announced in 1907 that he is going to make a car that is affordable to common people, there were many who doubted his words. He and other car manufacturers managed to do it nevertheless; today, the number of passenger cars in the world has reached 600 million.
Thousands of cars need thousands of parking spaces. There are not enough parking spaces in cities and settlements and, thus, the space in front of the houses is packed with cars. Additional parking space can be created only at the expense of sports grounds and playgrounds.
When arriving in a city by car, finding a parking space can be a real challenge since there are simply not enough parking spaces next to the sidewalks. Enterprises are also moving to the outskirts of cities or even beyond city borders because of the lack of parking spaces, making people even more dependent on cars.
Nobody had even heard of car parks in the 19th century. Today, incorporating parking areas and car parks into the city plan is one possibility to reduce the number of cars parked on city streets and courtyards – nobody wants to look out the window and only see a huge parking lot, to drive in circles in streets filled with cars, looking for a parking space, or walk on a sidewalk which is increasingly occupied by cars.